
What is a large language model, actually?
If you’ve used ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini lately, you’ve probably noticed they feel different than they did a year or two ago. They don’t just spit out answers instantly anymore; they often pause to “think” for a few seconds before responding. We’ve moved past the era of simple chatbots and into the age of the “reasoner.”
But what is a Large Language Model (LLM) at its core, and why has the way they work changed so much in late 2025? To understand what’s happening inside those digital brains, we have to look at how they were built and how they are evolving into something much more powerful than a fancy autocomplete.
Read more
What is a prompt and why does how you ask matter?
If you’ve spent any time with an AI chatbot lately, you’ve already written a prompt. Simply put, a prompt is the instruction or question you give to an AI model to get it to do something. It’s the digital equivalent of a person-to-person request, but instead of talking to a colleague or a friend, you’re talking to a vast network of statistical patterns that “understands” language.
As we head into 2026, the way we interact with technology has fundamentally shifted. We no longer just click buttons or select menu items; we use natural language to describe what we want. This shift has turned “prompting” from a niche technical curiosity into a core skill for anyone who wants to get things done efficiently.
Read more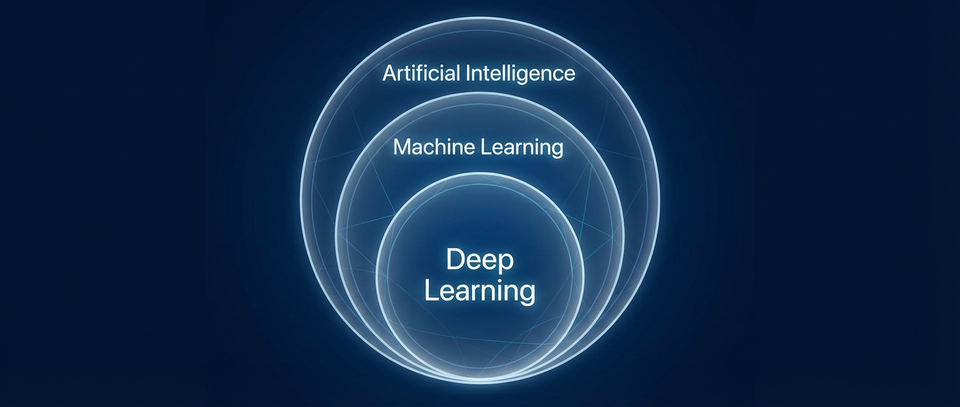
What's the difference between AI, machine learning, and deep learning?
If you’ve spent any time reading about technology lately, you’ve probably seen the terms “Artificial Intelligence,” “Machine Learning,” and “Deep Learning” used almost interchangeably. It can feel like a game of buzzword bingo where everyone is talking about the same thing but using different names to sound more technical.
The truth is that while they are closely related, they aren’t the same thing. Think of them like Russian nesting dolls: Deep Learning is a specific type of Machine Learning, and Machine Learning is a specific type of Artificial Intelligence. Understanding which is which helps clear up the mystery behind how your favorite tools actually work.
Read more
Why AI chatbots make things up: hallucination explained
If you’ve spent any time using modern AI like ChatGPT or Claude, you’ve probably had a “wait, what?” moment. You ask a question, and the chatbot gives you a perfectly formatted, highly confident answer that is completely, 100% wrong. In the industry, we call this “hallucination,” and it remains one of the most fascinating and frustrating quirks of artificial intelligence.
Even with the massive leap forward we’ve seen with “reasoner” models—which use test-time compute to “think” before they speak—AI still sometimes pulls facts out of thin air. It isn’t trying to lie to you; it’s simply doing exactly what it was designed to do: predict the next most likely word in a sequence. Understanding why this happens can help you use these tools more effectively and, more importantly, know when to take their answers with a grain of salt.
Read more
Why do AI tools have knowledge cutoff dates?
If you’ve ever asked an AI chatbot about a news event from this morning or a software update released last week, you might have been met with a polite apology. Even the most advanced AI models often admit they have a “knowledge cutoff” — a specific point in time where their internal database simply ends. It can feel a bit strange that a tool capable of writing complex code or summarizing history books doesn’t know who won the game last night.
The reason for this isn’t just a lack of an internet connection. It’s actually a fundamental part of how modern AI is built. To understand why your favorite AI tool is “stuck” in the past, you have to look at the massive, expensive, and time-consuming process that happens before you ever send your first prompt.
Read more